Translate this page into:
Aurora Borealis pattern: A clue to onychomycosis

*Corresponding author: Kurat Sajad, Department of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprosy, Government Medical College, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India. drkuratsajad@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Ul Islam M, Danusari S, Sajad K. Aurora Borealis pattern: A clue to onychomycosis. CosmoDerma. 2025;5:17. doi: 10.25259/CSDM_189_2024
Here, we report two similar cases of onychomycosis, which we diagnosed with the help of dermoscopy. Both patients, in their late thirties, with underlying type II diabetes mellitus, presented to the outpatient department with yellowish discoloration of their fingernails with duration of 3 and 15 months, respectively. On examination, we found parallel lines of yellow and white color involving the dorsolateral part of the thumbnail in both patients. Dermoscopy revealed a longitudinal striate pattern with regularly arranged parallel lines of yellow and white color, regular spacing, and diameter with an Aurora Borealis pattern, distal ruin pattern, and subungual hyperkeratosis. Potassium hydroxide mount was positive for fungal elements [Figures 1a and b, 2a and b].
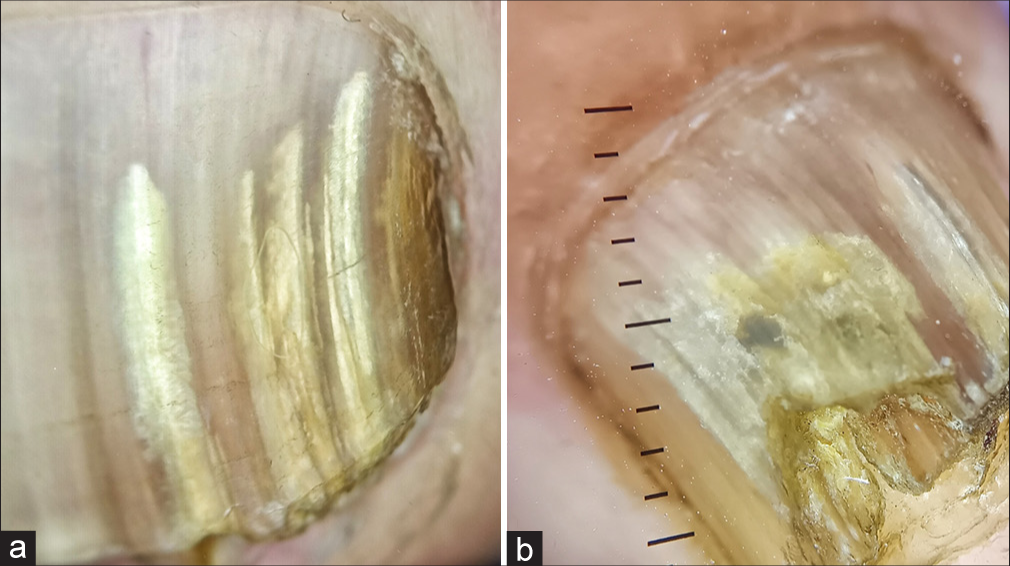
- (a and b) Dermoscopy revealing a longitudinal striate pattern with regularly arranged parallel lines of yellow and white color, regular spacing, and diameter with an Aurora Borealis pattern, distal ruin pattern, and subungual hyperkeratosis. Dermlite DL4,10×.
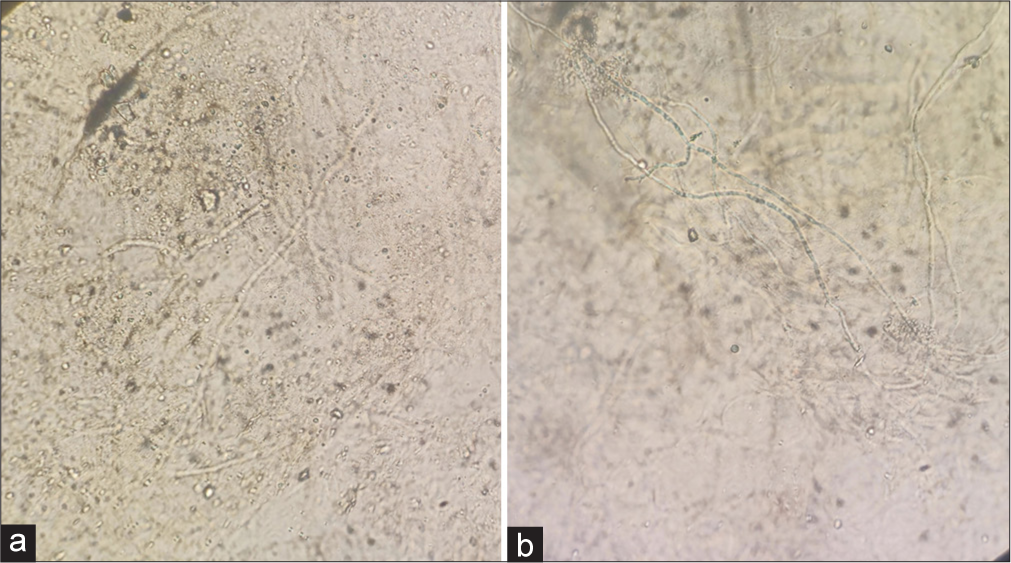
- (a and b) Potassium hydroxide mount positive for fungal hyphae.
Onychomycosis is a common fungal infection of the nail plate caused by dermatophytes or non-dermatophytes. It has an overall prevalence of 5% worldwide. Types include distal lateral, total dystrophic, proximal subungual, and superficial onychomycosis. Diagnosis usually involves microscopic examination with potassium hydroxide and immunofluorescent with calcofluor or fungal cultures. Dermoscopy is an important non-invasive tool that can give a clue to the diagnosis. Dermoscopic patterns observed include onycholysis, spiked pattern, chromonychia, white fluffy shadow, longitudinal and transverse striate pattern, subungual hyperkeratosis, and ruin aspect. In this report, we observed unique findings of Aurora Borealis, representing varying colors ranging from greenish-blue, bluish-gray, black, and whitish-yellow, representing fungal invasion and subungual debris.[1,2]
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Nail dermoscopy (onychoscopy) findings in the diagnosis of primary onychomycosis: A cross-sectional study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:341-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermoscopy of onycholysis due to nail psoriasis, onychomycosis and trauma: A cross-sectional study in skin of color. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2020;11:777-83.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





