Translate this page into:
Familial hypercholesterolemia

*Corresponding author: Ishan Agrawal, Department of Dermatology, Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi, India. ishanagrawal1995@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Agrawal I, Pal V, Sahoo B. Familial hypercholesterolemia. CosmoDerma 2023;3:161.
A 4-year-old female presented with multiple yellowish papules and plaques over knees, buttocks, legs, and gluteal cleft for 1 year, clinically diagnosed as xanthomas. Her mother had yellowish plaques in the bilateral periorbital region for 3 years clinically diagnosed as xanthelasma palpebrarum [Figure 1a].
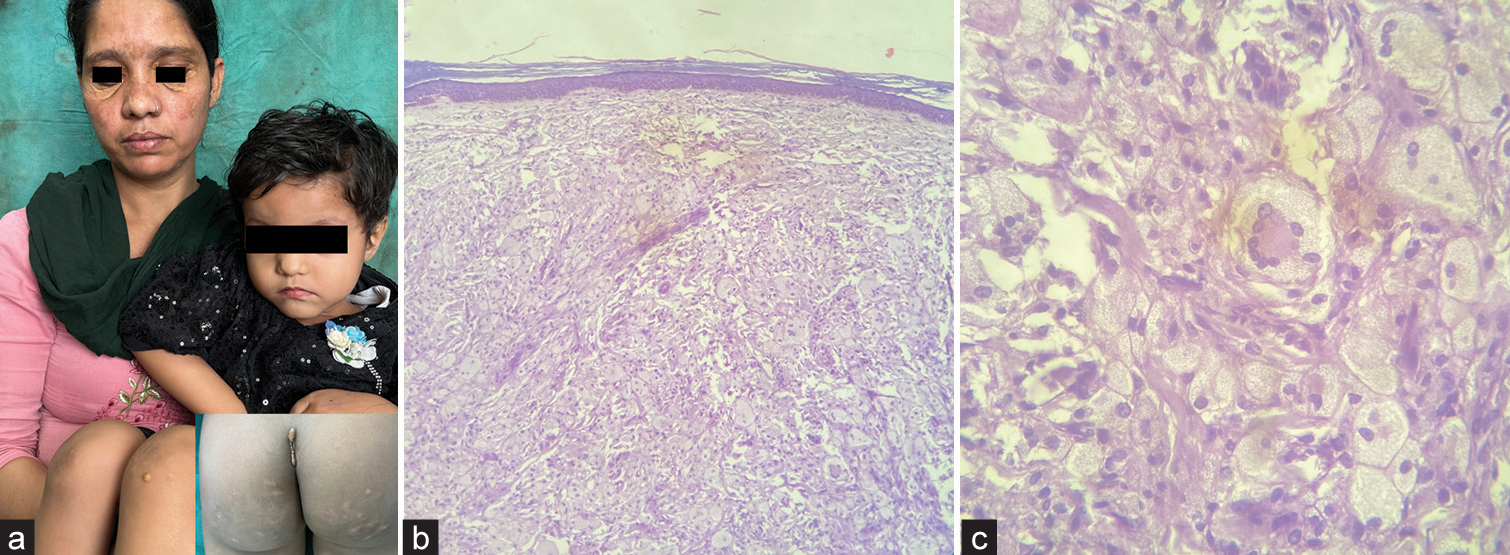
- Clinical image. (a) Daughter shows multiple yellow papules over the bilateral knees, legs, and gluteal cleft (Inset); and mother shows periorbital yellowish flat plaques. Histopathology showing (b) thin epidermis, flattened rete ridges, and lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in dermis and subcutis (H and E × 100). (c) Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and Touton giant cells (H and E × 400).
Lipid profile of daughter revealed raised cholesterol (804 mg/dL) and low-density lipoproteins (859.4 mg/dL). Lipid profile of mother showed raised cholesterol (329 mg/dL) and low-density lipoproteins (235.6 mg/dL). Histopathology from child’s knee showed multiple histiocytes, and lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate involving dermis and subcutis, consistent with xanthoma [Figure 1b and c]. Based on lesions, lipid profile, and histopathology, diagnosis of Type 2a dyslipidemia (familial hypercholesterolemia) was confirmed.[1,2]
Cutaneous manifestations reported with familial hypercholesterolemia include tendinous xanthoma (40–50%), xanthelasma (23%), and tuberous xanthomas (10–15%). Less commonly, subperiosteal xanthoma (below knee and over olecranon) may be seen. Rarely, intertriginous xanthomas in the finger webs, axillae, buttocks, antecubital, and popliteal fossa may also been seen, which are pathognomonic of familial hypercholesterolemia.[3]
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Familial hypercholesterolemia and its current diagnostics and treatment possibilities: A literature analysis. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58:1665.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Non-invasive detection of aortic and coronary atherosclerosis in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia by 64-slice multi-detector row computed tomography angiography. Atherosclerosis. 2008;197:910-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Familial homozygous hypercholesterolemia: Report of two patients and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:230-4.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





