Translate this page into:
Dermoscopy of herpes zoster

*Corresponding author: Arun Somasundaram, Department of Dermatology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India. arunsomasundaram25@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Somasundaram A, Ramar S, Ramamoorthy L. Dermoscopy of herpes zoster. CosmoDerma 2023;3:152.
A 65-year-old male sought consultation in the outpatient department for painful blisters over his upper back for 2 days. The patient was a known hypertensive and diabetic on medications. Cutaneous examination revealed grouped vesicles along the T1 (thoracic) dermatome on a slightly erythematous background [Figure 1]. There was a history of varicella in the patient during his childhood. Dermoscopy examination revealed pale pink cloudy polylobular structures with few lobules consisting of central brown globules on a slightly erythematous background [Figure 2a and b]. Tzanck smear showed characteristic multinucleated giant cells [Figure 3]. Diagnosis of herpes zoster (HZ) was made and the patient was initiated on oral tablet acyclovir 800 mg 5 times a day along with capsule gabapentin 300 mg once at night for 1 week for zoster-associated pain.

- Multiple grouped vesicles over the upper back on a slightly erythematous background skin along the T1 dermatome.
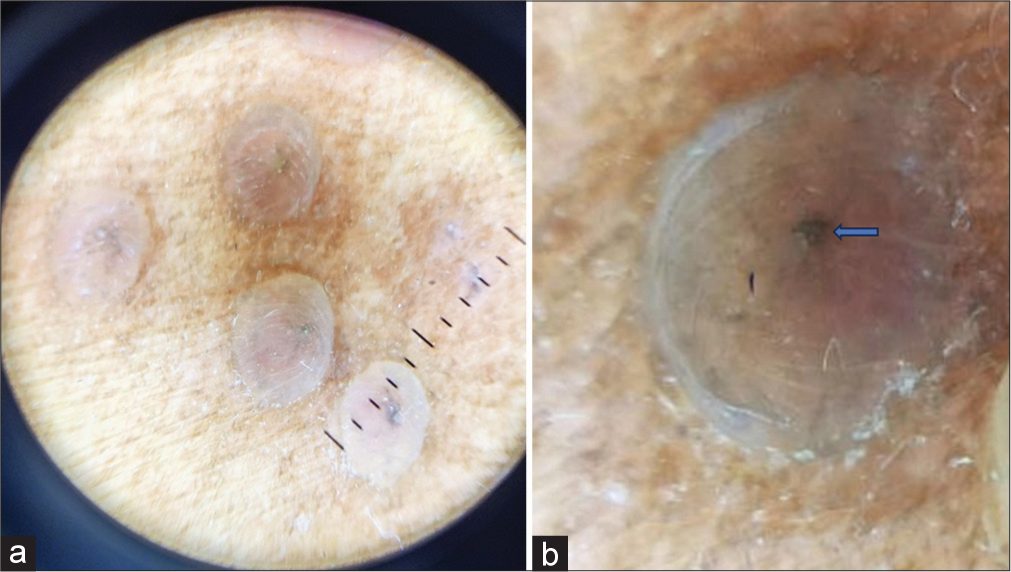
- (a) Dermoscopy (DermLite, × 10) Pale pink cloudy polylobular structures with few lobules consisting of the central brown globules, (b) Closer view of the central brown globules in the center of the lobule.
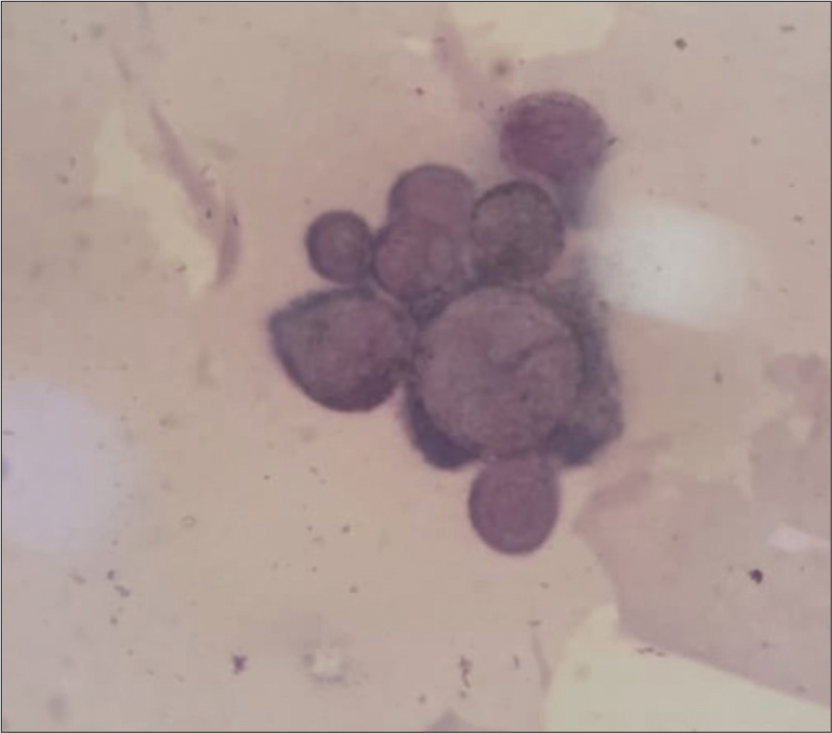
- Tzanck smear showing multinucleated giant cells.
Dermoscopy is a well-established tool as a noninvasive diagnostic modality. Diagnosis of HZ is usually easy and occurs with just clinical evaluation; however, recognition of atypical HZ can be a challenge for clinicians. Dermoscopic patterns described in the literature include white polylobular structures followed by meliceric crusts and erythematous backgrounds. The brown globules in the center of the polylobular structures as seen in our patient might represent the beginning of crusting in some lesions. It facilitated an early diagnosis by 1.62 days.[1] It is a useful tool to allow an early diagnosis and offer prompt treatment with antivirals when the clinical presentation is uncommon.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent is not required as patients identity is closed or compromised.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Dermoscopic features of herpes zoster: Case series and review of the literature. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023;13:e2023149.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





